Engineering Drawing
In my previous blog, I discussed the Concept of Design and Engineering Design Process. In this blog, I’m going to discuss the most important skill required by a Design Engineer to transform an Idea into Reality. This is the ability to create and read Engineering Drawing. Engineering Drawing is often called as a technical drawing. Through this blog, I’ll explain the basics of engineering drawing techniques. If you want to read my previous blog on Engineering Design Process.
So let’s start with the most basic and important question.
What is Engineering Drawing?
ENGINEERING DRAWING is a graphical representation of the actual design of physical objects with the details of its shape and features. An Engineering drawing is a graphical representation of an object, or a part of it, and is the result of creative thought by an engineer or technician. Ideas can be communicated from one mind to another with the help of Engineering Drawing. This method of communication is known as GRAPHIC COMMUNICATION. It is the process when one person sketches a rough drawing in giving direction to another person. Graphic communication contains the use of visual materials in order to explain ideas. Drawings, photographs, slides, transparencies, and sketches are all different forms of graphic communication tools. Any method that uses a graphical image to help in communicating a message, instructions or an idea is the process of graphic communication.

Engineering Drawing is by far the oldest type of graphic communication which is still used by each and every technical professional. It is been into practice since ancient times. But Leonardo da Vinci created the foundation of modern engineering drawing at a time when the Industrial Revolution was in its initial phase and he did it with its precise conventions of orthographic projection and scale. While this method was brought into effective use by Gaspard Monge.
For Free, Demo classes Call: 8149467521
Registration Link: Click Here!
History of Engineering Drawing
Gaspard Monge, a French mathematician who was also known as Father of descriptive geometry, faced the problem in creating Engineering drawings when he started working as an Engineer in the French Military. He developed a system that could be used to communicate details of an object to anyone across the world. This system is known to us as Orthographic Projection. It was quickly adopted by army engineers. However, France was at war at that time and Monge’s system was kept top secret for many years. It wasn’t until 1794 that Monge was allowed to publish and teach his system. This system spread across and revolutionized the world industry in a short amount of time.

The Journey of this Engineering Drawing Method is stated in the 5 stages as below.
- 1300-1500 Renaissance period: Perspective drawing technique was invented.
- 1765: Gaspard Monge Invented Descriptive geometry.
- 1770-1850 Industrial Revolution period: Orthographic projection technique was invented
- 1980s: 2-D CAD systems were developed
- 1990s: 3-D CAD systems were developed
What is the need of Drawing?
IMAGINATION is the key skill required while studying engineering drawing and so are the expertise in the field of Technical Drawing. It is very important to master this skill for all engineering professionals. The ability to create and read engineering drawings is the most important skill required of all technical people in the engineering profession.
What are the Standards/Rules followed while drawing?
Drawing standards are a set of rules that are followed while representing the technical drawings. These are used to make drawing communication easy to understand by everyone throughout the world.
Lines on an engineering drawing describe more than just the geometry of the object and it is important that the appropriate line type should be used. Basically 4 types of lines are used in the representation of the diagrams they are
- Visible line: represent features of the drawing that can be seen in the current view
- Dimension line; Extension line; Leader line: used for indicating the sizes and location of features
- Hidden line: represent features of the drawing that cannot be seen in the current view
- Centerline: represents the line of symmetry, a path of motion, centers of circles, an axis of the axis-symmetrical part

You will require two Line Thicknesses for most engineering drawings, a thick and thin line. It is usually recommended that thick lines are twice as thick as thin lines. A thick continuous line is generally used to represent visible edges and outlines. A thin line is usually used for short center lines, hatching, leader lines, dimensions, and projections.
Different Line Styles are used to clarify important features on drawings such as:
- Thin chain lines are commonly used on engineering drawings to indicate center lines.
- Centerlines are generally used to identify the center of a circle, cylindrical features, or axis of symmetry.
- Dashed lines are mostly used to show important hidden features for example wall thickness and holes.
For Free, Demo classes Call: 8149467521
Registration Link: Click Here!
What are the types of views?
- Orthographic Projection
Orthographic Projections are a collection of 2-D drawings that combine together to give an accurate overall representation of an object. It is a type of engineering drawing which includes different views of an object projected on different reference planes such that the person is observing in the perpendicular direction to the respective reference plane. 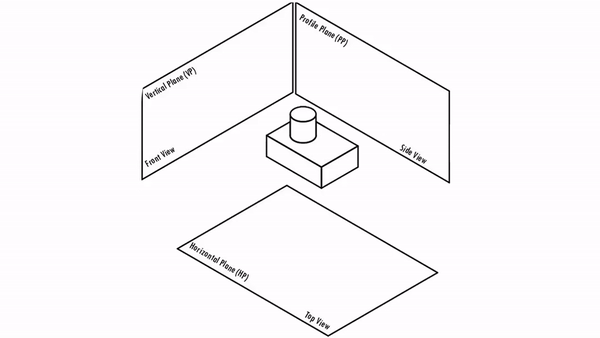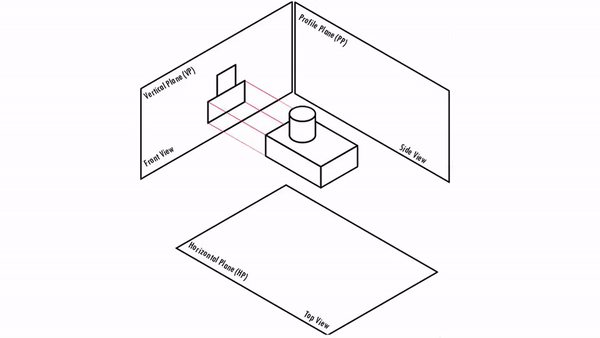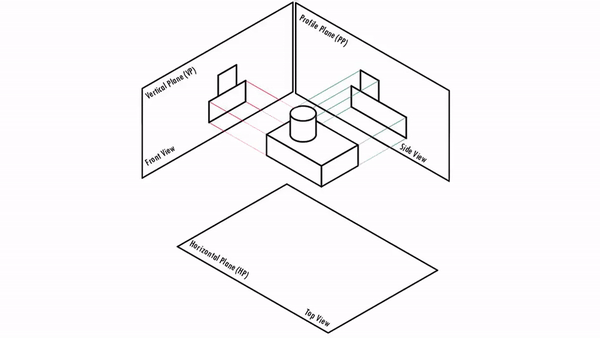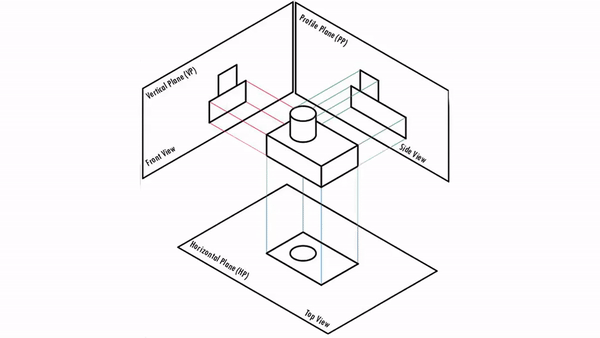
Different Reference planes are
- Horizontal Plane (HP)
- Vertical Plane (VP)
- Side or Profile Plane (PP)
Different views are
- Top View (TV) – Projected on HP
- Front View (FV) – Projected on VP
- Side View (SV) – Projected on PP

Isometric
In the field engineering, technical professionals often draw two or more than two orthographic projections to provide the details of the shape and size of the object. But sometimes, a technician with less experience often requires hard exercise of the brain in order to visualize the orthographic projections. To make this process easy and to understand the shape of the object, the Engineering Drawing needs an additional view known as the Isometric view. The isometric view represents the overall appearance of the object and makes it easy to understand some details which may be difficult to understand in the orthographic projections.
Isometric View is the 3D View of an object provided on a plane of projection in which all the projection elements are parallel but inclined at an angle of 30-degree angle to the plane of projection. In this type of projection method, the object is placed in such a position that all the three axes make an equal angle with the plane of projection
Isometric drawing is important technique for engineering designers as this drawing clearly shows the exact shape and features of the object that has been designed.
- It is also useful for product and equipment manufacturers as they can easily understand the method of construction of an object or equipment.
- This type of drawing can also help the beginners, fresher or someone who has no basics in engineering drawing, unlike orthographic drawing.

Perspective
The meaning of the word “perspective” is the proper relative position of objects as seen. Perspective drawing is the only drawing which represents the complete object as it would appear to an observer. It is the representation of an object on a plane surface as it would appear to the observer’s eye when viewed from a fixed point.
Different types of Perspective views are:
- One Point Perspective View
- Two Point Perspective View
- Three-Point Perspective View
- Four Point or Zero Point Perspective View
We will discuss these views in detail in my next blog.
For Free, Demo classes Call: 8149467521
Registration Link: Click Here!
Orthographic Projection Methods
- First Angle Method
In this method, the object is placed between the observer and the reference planes such that it rests in the first quadrant. Now parallel projections are generated by keeping the observer in three positions w.r.t to the object. That is Front, Top and Side. Now when the projections are created the planes are rotated to create a flat sheet as shown below.

- Third Angle Method
In this method, the reference planes are placed between the observer and the object such that the object rests in the third quadrant. Now parallel projections are generated by keeping the observer in three positions w.r.t to the object. That is Front, Top and Side. Now when the projections are created the planes are rotated to create a flat sheet as shown below.

Dimensions (structure and parts)
A dimensioned drawing is used to provide all the information necessary for a finished product or part to be manufactured. For example, a dimension is shown below.

Dimensions are always drawn using continuous thin lines. Two Extension lines indicate where the dimension starts and finishes. Extension lines do not touch the object and are drawn a perpendicular to the element you are dimensioning. All dimensions less than 1 should have a leading zero while it should be written as 0.65 and not as .65. Parallel dimensioning usually consists of several dimensions originating from one projection line.
The Structure Of a typical Dimension is as shown below. It contains one dimension line, two extension lines and a text box which generally represents the numerical value of the dimension. Fig below shows the normal structure of a Drawing Dimension.

- Title Block
The title block of a drawing is usually located on the bottom or lower right-hand corner of the drawing sheet. It contains all the information necessary to identify the drawing and verify its validity. A title block is divided into several sections. These sections mainly contains drawing title, drawing labels, drawing numbers, list of the locations, site, and vendors. It also includes the Date, Designer name, Company title, etc.
The Drawing title, revision number, sheet number are used for identification and filing purpose. Usually, the number is unique to the drawing and is in the form of code that contains drawing information.
For Free, Demo classes Call: 8149467521
Registration Link: Click Here!
Drawing layout all engineering drawings must contain a title block. The title block should include:
- Title:- Title of the drawing
- Name:- Name of the person who produced the drawing
- Checked:- before manufacture, drawings are usually checked
- Version:- many times drawings are revised, each revision must be noted
- Date:- the date on which the drawing was produced or last revised
- Notes:- any note relevant to the drawing
- Scale:- the scale of the drawing
- Company name:- Name of the company
- Projection:- the projection method (1st angle or 3rd angle) used to create the drawing views
While creating a title block for the drawing sheet background borders enclosed by the edges of the trimmed sheet and the frame limiting the drawing space shall be provided with all sizes. It is usually recommended that these borders have a minimum width of 20 mm for size A0 and Al, and a minimum width of 10 mm for size A2, A3, and A4. Four centering marks should be provided on all drawings in order to simplify the positioning of the drawing when reproduced.

- Use of Technology in Engineering Drawing.
Since the method of graphic communication by using engineering drawings have evolved and become popular over the years, many technologies have been developed to make this task easy. Engineering designs are quite complicated and while earlier engineering drawings were handmade, today we use different types of software applications. To solve most of the engineering problems, it requires a combination of organization, analysis, problem-solving principles and a graphical representation of the problem. Since an Engineering drawing is precise and communicates all information of the object clearly, it has to be flawless. This is why we need CAD. As the computer power in the latter part of the twentieth century increased, with the arrival of minicomputer which runs on a powerful microprocessor, has allowed design engineers to use CAD files that represent the dimensions and properties of the object accurately.
For Free, Demo classes Call: 8149467521
Registration Link: Click Here!
Types of CAD Software
Since its first introduction in the late 1960s, CAD software has improved a lot. They are broadly classified as:
- 2D CAD
- 3D CAD
- 3D Wireframe and Surface Modelling
- Solid Modelling
There is a huge growing demand for CAD software as more and more companies (if not all) are turning to CAD / CAE / CAM to achieve efficiency, accuracy and reduced time-to-market of products. The industry leaders in this field include AutoDesk, Dassault System, Siemens, PTC, and Altair.
Author:-
Vijay Gujar
Call the Trainer and Book your free demo class for now!!!
© Copyright 2019 | Sevenmentor Pvt Ltd.