Engineering Drawing
Introduction
In my last blog, I covered the concepts of Engineering Drawing. In this blog, we will continue to discuss the topic without which our engineering drawings are incomplete. This blog will cover the structure of the Engineering Sheet Background and Title Block in detail. I’m explaining this topic because the Title block is a vital part of engineering drawing and it plays a very important role in the process of documentation.
If you want to understand the process of engineering Drawing Click Here
A little Recap of Drawing Sheet
Originally Engineering drawings have been known as blueprints. This is because of the original method of printing these drawings that used a chemical process which resulted in white lines on a blue background or vice versa. This process has become obsolete for a long time. However, the name “blueprint” is still often used to describe engineering drawings.
Today engineering drawings are prepared with the use of specialized computer programs known as CAD programs. High-quality engineering drawings are essential to reduce the errors in engineering process. A good engineering drawing accurately represents design features like the geometry, dimensions, tolerances, material, and finish associated with a given engineered component. The use of a variety of different viewpoints and detailed “cuts” (or cross-sections) ensures that an appropriate level of detail is communicated to the fabricator.
For Free, Demo classes Call: 8149467521
Registration Link: Click Here!
Types of drawing sheets
This topic was covered in my previous blog Click Here. The types of drawing sheets that we are going to use are called A- series drawing sheets. These are mainly 5 types.
- A4 – 297mm x 210mm (this is the smallest sheet)
- A3 – 420mm x 297mm
- A2- 594mm x 420mm
- A1- 841mm x 594mm
- A0- 1189mm x 841mm (This is the Largest sheet)
What are the standards?
There are different standards used while creating the drawing sheets. These Standards provide rules for drawing specification and interpretation. Standardization also helps in communicating internationally, because people from different countries who speak different languages can read the same engineering drawing, and interpret it the same way with the help of standards.
- ANSI – American National Standards Institute
- ISO – International Standards Organization
- JIS – Japanese Standards
- BIS – Bureau of Indian Standards
For Free, Demo classes Call: 8149467521
Registration Link: Click Here!
Drawing Sheet Background
A typical Engineering Drawing sheet contains many things other than the drawing views. Certain rules are needed to be followed while creating the engineering drawing sheet. I will discuss all the parts of sheet background in detail for better understanding.
Sheet Border: – while preparing any sheet for drawing a sufficient margin should be provided.

Drawing Space: – This is the space in which we place all the views required to specify the design of a Mechanical component. There are different types of views which can be found in the Drawing space such as-
- Orthographic Views (Multi View Drawing),
- Isometric Views,
- Perspective Views,
- Auxiliary views
- Oblique projection
- Section Views (Cross Section and Half Section),
- Detailed Views.
Drawing Scale
Scale is the ratio of the dimension of a drawing of an object which is drawn on the sheet to the actual dimension of the same element in the real world. Scale is generally used to fit the drawing on the drawing sheet without disturbing the actual proportions of the sizes of the object.
SCALE is followed by the indication of its ratio, as follow
- SCALE 1:1 is used when drawing sizes are equal to actual sizes.
- SCALE X: 1 is used to enlarge scales (X > 1) i.e. when drawing sizes are larger than the actual sizes of the object.
- SCALE 1: X is used for reduction of the sizes (X > 1) i.e. drawing sizes are smaller than the actual sizes of the object.
The dimension value which are shown in the drawing are generally corresponds to “actual size” of the object and they are independent of the scale used in creating that drawing. Always Take scale as recommended, if not you must choose a suitable scale as per the drawing requirements. When you design a part or assembly model, you can build the model to the actual scale of the real-world object that you are creating. Whereas the size of the working drawing sheet determines the scale that you should use to display the 3D part or assembly model on the drawing sheet. For example, the drawing view scale for a Engine part would be smaller if an A3 size sheet were used, because the A3 size border is smaller than the D size. Whereas the dimensional values of the parts or assembly models in your part views measure the actual size of the model. For example, if the dimensions of a hole feature in a part is 25 mm and the drawing view scale is 2:1, then if you dimension the hole feature, it will be 25 mm, not 50 mm. This means that while using proper scale you never have to worry about the part sizes affecting the dimensional values when you are creating a drawing. The dimension and annotation sizes in your working sheets are always independent of the drawing view scale.
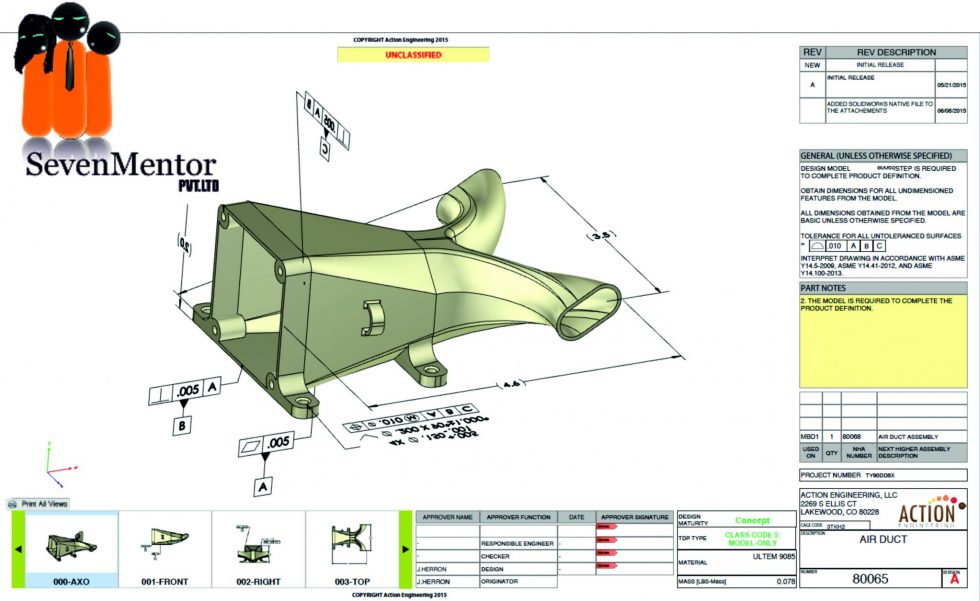
What is Title Block?
The title block provides a range of information relating to the drawing. This helps to identify the drawing and it plays an important role in drawing documentations process. Generally a design engineer uses title block to ensure the design cannot be stolen and to protect the copyrights of the design. Normally Title block includes –
- the name of the company,
- the name of what is drawn,
- the drawing sheet: number for storage and; reference purposes,
- who drew the drawing,
- who checked the drawing, and
- 0ther important information regarding the drawing, along with complete description of any changes that have been made since earlier drawing was originally, drawn.
- Each company has its own title block.
Different parts of the title block are explained below along with their purpose in the drawing sheet and how they are effectively used in the drawing sheet.
Standard Design and Parts of title Block
Generally following parts should be present in the title block in order to provide complete information related to any kind of design.
- Enough orthogonal views: There should be enough views in order to provide adequate describe the component. This helps to understand the features of the component in detail.
- Dimensions: There must be evenly distributed dimensions. It should be structured properly so that the detailed information about the sizes of the drawing can be provides. Also proper care should be taken to avoid duplicated dimensions.
- Scale: Use of proper annotative scale is recommended while drawing. Appropriate scale must be used to fit the component onto the drawing sheet. For example
- 1:1,
- 1:100,
- 1:500 or
- 1:1000
- The type of projection: Which projection method is used while creating the drawing views should be mentioned properly with their symbols
- First Angle Projection Method and Third Angle Projection Method.

- The name or title of drawing: The name of the drawing must be mentioned properly of the component? The title refers to the content of the document. More detailed information, for example details regarding source, adaptation to market, standard or environmental conditions, which may be given in the supplementary title. Generally titles which are specific to a particular part use or application should be avoided. The title should be chosen from drawing related terms, such as those given in international or national standards, company standards, or according to practice within the area of application. Clear and detail descriptions helps in efficient searching and retrieval using the title field. Also abbreviations should be avoided.
- The drawing number: A proper Serial number should be mentioned to each drawing. This drawing number is unique and is used for identification of the drawing (in-house system) of the component? The drawing identification number is referred for part identification and to conveniently store and retrieve the drawing and the produced parts. The identification number is always unique at least within the company of the legal owner. While there is no set way to assign part numbers, common systems are non-significant, significant, or some combination of the two previous systems.
- Dimensional units used should be mentioned in a proper note wherever required (mm, m, inches, feet etc.)
- Tolerances: An accurate drawing should be able to explain what are the manufacturing tolerances for each part of the component? Hence proper GD&T symbols must be used wherever necessary.
- Reference to assembly drawing: What does the design component assembles into?
- Material: Information regarding the type of material and its properties with which the component is manufactured from need to be provided.
- Drafter: who created drawing?
- Checker: who checked drawing?
- Approver: who approved drawing
- The date of issue for the drawing is the date on which the document is officially created for the first time, and that of every further released version. It is the date when the drawing is made available for its intended purpose. The date of issue is very important for legal processes, e.g. patent rights, traceability.
- Zones: Where is the reference zone that drawing is referring to?
- Revision: What changes has been revised and why they are made along with the revision is this drawing should be mentioned.
- Sheet Size: which page size is used like A4, A3, A2, A1 or A0
- Company Name and details along with address and contact
For Free, Demo classes Call: 8149467521
Registration Link: Click Here!
All this points are listed below in the form of an example so that you can get an idea how the sheet background and title block should be constructed.
Author:-
Vijay Gujar
Call the Trainer and Book your free demo class for now!!!
© Copyright 2019 | Sevenmentor Pvt Ltd.